Cucumbers in Russia are grown everywhere, both in the southern regions and in greenhouses in the north of the country. In addition to the well-known old varieties of cucumbers, breeders have bred hybrids characterized by high productivity and resistance to disease. In this article, we will talk about the hybrid of the Cedric F1 cucumber, its characteristics and description will be given, as well as methods of growing and caring for the crop.
Characterization and description of the variety

Cedar Cedric is a first-generation hybrid, so immediately after the name you must specify the F1 mark.
Cedric F1 appeared thanks to the work of Dutch breeders, employees of Enza Zaden. This is a hybrid of early ripening, allowing you to get an early harvest of fruits.
There are no male flowers on the cucumber hybrid; all the flowers on the plant are female, with an ovary already present.
Cucumber grows without the need for any pollination or fertilization, this phenomenon is called parthenocarpy.
Fruits contain only a few dozen thin, hollow seeds, not capable of reproduction.
Pollination with bees or bumblebees for Cedric F1 is even undesirable, as the result may be coarse fruits containing full seeds.
Features of the bush and fruits
In this hybrid of cucumber, the stem is powerful, the leaves are large, soft, rough on both sides of the leaf plate, green. The main crop of the plant is increased on the lateral stems located on both sides of the central stem. Hybridization of the hybrid is average, the bush is indeterminate, that is, not limited in growth, therefore, it will grow as long as the grower allows it or before freezing temperatures.
Important! The gardener must remember that the usefulness of seeds collected from hybrids is the apparent, the next generation of vegetables obtained from them will be diverse, and the yield of plants is weak.
The fruits of the Cedric F1 hybrid are small, dark green, with whitish implicit stripes, covered with pimples. The diameter of the fruit does not exceed 3–3.5 cm, the length of green leaves varies from 12 to 14 cm. The fruit pulp is dense, without voids, crunchy, and genetically has no bitterness. The average mass of greenery is from 100 to 110 g.
 Cucumbers are suitable for fresh consumption, and are also used for pickling and pickling.
Cucumbers are suitable for fresh consumption, and are also used for pickling and pickling.
Fruitfulness
The productivity of the Cedric F1 hybrid is very high precisely due to the bundle ovary. From 2 to 4 cucumbers develop in each bunch. With 1 m², the grower can collect up to 15 kg of hybrid fruits, of course, subject to all the subtleties of agricultural technology. Originators recommend growing 3–3.5 plants of Cedric F1 on soil per 1 m².
Did you know? The ancient Roman emperor Tiberius demanded to his table daily, throughout the year, fresh cucumbers. For this reason, palace gardeners invented mobile greenhouses for cucumbers, which were exported to the sun during the day and delivered to the room by servants in the evening.
Ripening and flowering periods
The first flowers on the plant appear after about 30 days of growing. In greenhouses, the flowering and fruiting of cucumber plants occurs several weeks earlier than in open ground.
Maturation in the bunch is not simultaneous, but sequential, one after another. The first cucumbers ripen 40–45 days after emergence of sprouts from the soil. At the same time, no more than 5 fruits ripen on the bush.

Pluses and minuses
- Hybrid Cedric F1 has the undoubted advantages:
- large crop;
- early bearing
- tasty and quality fruits;
- bundle bearing;
- good taste of greens;
- lack of bitterness;
- resistance to stress temperatures;
- immunity to certain diseases (cladosporiosis, cucumber mosaic virus and powdery mildew).
- The disadvantages of the variety:
- the high cost of seeds and the inability to independently collect planting material;
- mandatory bush formation.
Video: the experience of growing cucumber Serdrick in the Volgograd region
Sowing and growing technology
It is best to start growing cucumbers when the spring temperature has established and is kept high enough even at night. At this time, during the day, the temperature should not fall below + 20 ° C, and at night - below + 15 ° C. It is even better to grow cucumbers in a place where the temperature is constantly kept in the range of +20 ... + 22 ° C. It is advisable to start growing seedlings 3-4 weeks before the time of planting comes to a permanent place.
Growing cucumber seedlings:
- It is best to use planting pots with a diameter of 12 cm. Pots should have a hole in the bottom to drain excess moisture after watering. Also, each pot should be equipped with a fairly deep tray that protects window sills and seedlings from moisture. Cucumbers do not tolerate the anxiety of the root system, and react to this by stopping growth for up to 2 weeks. Therefore, it is advisable for the gardener to grow glasses of organic (peat or humus) for growing cucumbers. This planting container decomposes perfectly in the ground, being placed, together with the plant, directly in moist soil.

- The soil for cucumber seedlings is purchased in gardens in stores or mixed independently at home. For a home mixture of soil, they are taken in equal parts: coarse sand, fertile soil and humus. Also, several handfuls of wood ash sifted through a sieve obtained from deciduous wood can be added to the soil mixture.

- The soil is poured into planting pots a little more than half the volume. After the cucumbers begin to grow, the soil will be gradually added by the grower directly under the root of the plant until it reaches the edge of the planting capacity. The soil in the pots is well moistened and allowed to warm for several days at room temperature. When the temperature of the sowing soil warms up to + 20 ° C, you can start planting seeds.
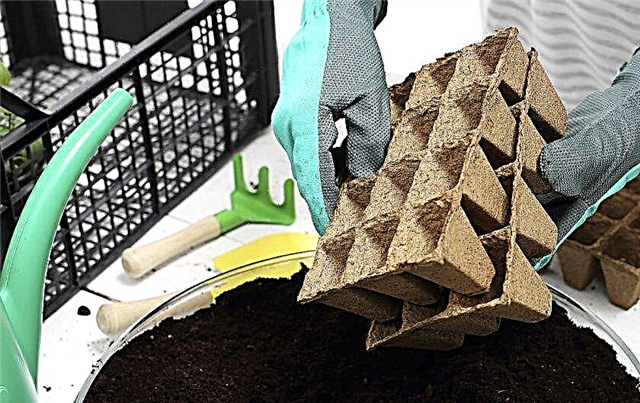

- In the soil of each tank, two planting holes are made with a depth of 1 to 1.5 cm. The seeds of the cucumber are laid out in the planting pits and covered with soil. After planting, the soil is very moderately watered. It is enough to moisten slightly, it is not necessary to fill the soil so that water flows through the drainage holes. Excess moisture can cause seed rot. 7-10 days after germination, only the strongest plant is left in the pot. The extra seedling is not pulled out of the soil, but carefully cut with scissors at the border of the soil.
- Pots with crops are put in a warm place for 3-4 days. After the appearance of sprouts, the landing containers are transferred to a well-lit place (on the south window or under a special lamp).

- The main conditions for growing good seedlings are to maintain heat in the room and prevent dehydration of the plant. It is not necessary to water cucumber seedlings too often, but also to prevent the plants from withering. When watering, you need to carefully monitor that moisture does not fall on young plants, as this threatens the development of powdery mildew. Also, too much moisture under the root of the seedlings can lead to the formation of a black leg, leading to the death of the cucumber. To prevent evaporation of moisture from the soil lump, the pot with seedlings can be covered with a transparent plastic wrap. A thin cling film is perfect for this. Also, direct sunlight is undesirable for seedlings, so you can slightly shade plants with the help of a newspaper.

- During the cultivation of a cucumber, the room should always be kept at the same temperature so that the plants grow in a smooth rhythm. A sharp increase in temperature leads to a rapid increase in above-ground mass, stretching of the stem and leaves. Cold night temperatures lead to stunting and weaken the plant, after which fungal spores and root rot are activated.
- During the growing season of cucumbers in the room, plants need hardening, adapting them to future planting in a permanent place. To harden the first weeks of life, it is enough to open the window for a period of 15 minutes to half an hour, later, when the temperature in the street is not lower than room temperature, the plants are taken out into the open air. Street hardening starts from 30 minutes and gradually, over time, extends to full daylight hours.
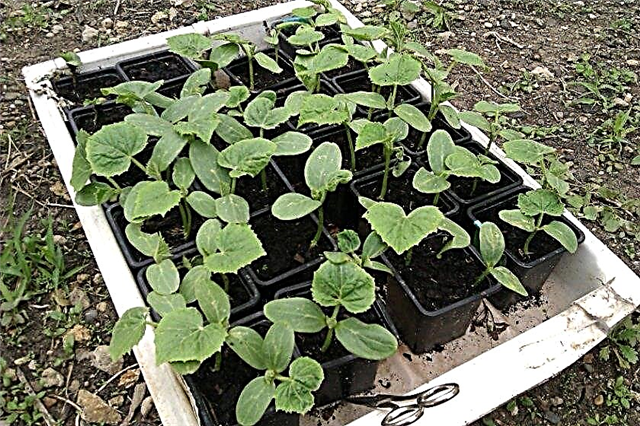

- Cucumber seedlings remain in the pots until 4-6 true leaves are formed in the plants. Seedlings of cucumbers during growth in pots are supported vertically with the help of special support pegs.
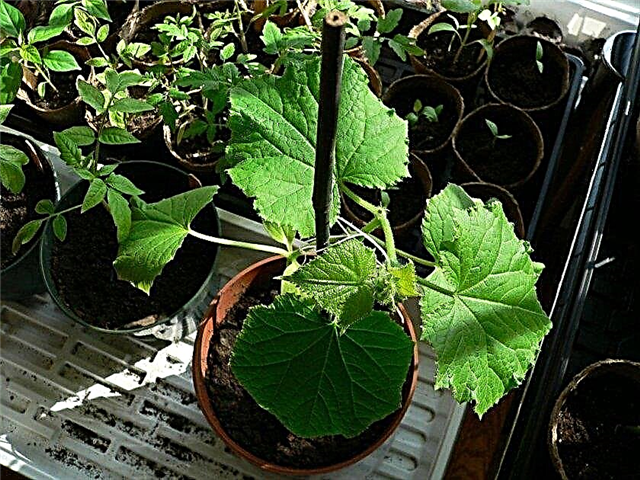

In the open ground
Cucumber seedlings or seeds can be planted in the soil when the soil warms up to at least + 15 ° C. At this temperature, you can already consider planting, although the ideal temperature for a cucumber is a soil temperature of + 18 ° C. But the air temperature, especially at night, should be quite high.
Cucumber seedlings are planted in open ground closer to June 1 to exclude the possibility of returning night frosts. When planting, you need to avoid crowding in the garden, as the culture has large leaves. The less often plants are planted, the less likely the occurrence of diseases. Plants are planted with a pot (from peat, humus or paper).
Important! You can grow cucumbers in several terms, for example, to plant the first garden in mid-May, and the second - in early July. This will allow you to get a fruit crop until late autumn.
When transplanting, you need to carefully consider that the soil does not come into contact with the stem of the plant. After planting, the bush is watered with warm water. The roots of a young plant should always be in warm, slightly moist soil.
Cucumbers need to be tied to a support. The easiest garter option is a vertically attached cord. The cord is tied with a free knot to the lower part of the plant and to a support wire located at a height of about 2 m. Weekly, the cucumber stem is wrapped around the cord.
In open ground, plants are grown according to a looser scheme than in a greenhouse. On a cucumber bed 60 cm wide, only 1 row of plants is grown. It is centered along the bed. In this case, the distance between plants from 20 to 25 cm is observed.
If the width of the beds exceeds 120 cm, 2 parallel rows of cucumbers can be grown on it. Moreover, the distance in each row between plants is maintained from 20 to 30 cm, the cucumbers of the first row are arranged in relation to the cucumbers of the second row in a zigzag (staggered).
A checkerboard layout allows plants to get more lighting and better ventilation. For vegetative cucumbers, it is necessary to establish support in the form of a longitudinal trellis up to 2 m high. A two-row planting of plants can be supported with a common trellis placed between these two rows.
Landing in the greenhouse
In central Russia, cucumber seedlings can be planted in an unheated greenhouse from May 1, in cooler areas it is better for a gardener to wait until May 15. At the same time, you can sow the seeds of cucumbers, but plants grown through seedlings will develop more vigorously, give a higher yield and less suffer from pests and diseases.
 Since the space of greenhouses must be saved, the cultivation of cucumber bushes in the greenhouse is carried out according to a denser scheme than in open ground.
Since the space of greenhouses must be saved, the cultivation of cucumber bushes in the greenhouse is carried out according to a denser scheme than in open ground.
In the greenhouse, cucumbers are planted in both 1 and 2 rows, depending on the width of the greenhouse. When planting in 2 parallel rows, the bushes are arranged in a zigzag with respect to plants of the opposite row. The distance in the row between the cucumbers is 10-15 cm.
So that such a minimum distance does not create excessive planting density, the grower has to remove leaves on the plants. The lower 5-6 leaves are removed completely, so that 1 central stem remains.
In the future, the leaves will also be thinned out, but not so dramatically: out of 3 grown leaves, about 1 will be left on the stem. This will allow air to circulate freely between the plants in the greenhouse, as well as cucumbers will be fully illuminated, which is important for setting and further fruit development .
Care Features
Throughout the summer, cucumber plantations should be regularly looked after. Leaving consists in timely processing of the soil (weeding and loosening), irrigation, formation of a bush, garter of plants, mulching, protection from insects and diseases.
Watering and fertilizing
During fruiting, cucumbers need to be watered. On street beds, the frequency of irrigation depends on the weather, if there is no rain, then it is enough to water the cucumbers twice a week. When growing under the roof of a greenhouse, each plant should get at least 2 liters of moisture for irrigation.

In greenhouses and hotbeds, plantings are watered with the help of root canals or a branched drip system. Drop watering helps to save water, and apply it exactly under the root of each plant.
Organics is a fertilizer well absorbed by cucumbers. On the soil enriched with cattle manure or compost, yields will be several times higher than on scarce soil.
Also, cucumbers can be fed during the growing season with a small amount of nitrogen and potassium in mineral form. Nitrogen supports the growth of lush leaves, and potassium gives the hardness of cucumber pulp and the dark skin of the fruit.
Important! If the feeding procedure is not combined with irrigation, but is carried out separately, then the gardener needs to remember that all liquid fertilizers are applied only on moist soil, that is, after irrigation.
To feed cucumbers, you need to sprinkle 60 g of ammonium nitrate and 30 g of potash fertilizers in the root zone of plants, on an area of 1 m², then loosen the soil, while mixing the fertilizing with the ground. You can also dissolve fertilizers in water for irrigation and serve under the root of cucumbers.
Depending on how quickly the bush builds up the crop, the plant is depleted. Therefore, during fruiting, the cucumber bed requires periodic top dressing. Usually the first top dressing is carried out during the flowering of bushes.

Next, plants need to be fed every 2 weeks throughout the summer. It is most convenient to use liquid organic fertilizer for top dressing. It can be prepared at home from bird droppings. For these purposes, droppings of any birds are suitable, for example: ducks, chickens, pigeons, geese or ostriches.
Dry or fresh organics are mixed in equal parts with water, and then left to ferment for a couple of weeks in a tank with a lid closed. Close the tank so that nitrogen does not evaporate from the fertilizer. Every day, the solution is stirred, provoking the release of carbon dioxide.
Important! An open container with a roaming solution of bird droppings and water, installed in a greenhouse with growing cucumbers, will be an excellent stimulator of fruiting for the crop. Cucumbers are very fond of carbon dioxide, which will constantly fall into the air of the greenhouse from the solution tank.
Ripe and ready-to-use concentrated fertilizer does not release bubbles onto the surface. Concentrated dressing is poured under the root of the plant, previously diluted with clean water. Approximately a bucket of water is added to 500 ml of concentrate. For feeding one plant, 2 l of liquid is enough.

Garter and bush formation
The formation of a cucumber bush depends on the method of growing this crop. If cucumbers are grown without a garter, “spread”, that is, lie on the ground - gardeners are not involved in their formation. When growing on a trellis of a street bed and in a greenhouse, cucumber bushes are necessarily formed by truncating the growth points of the side or main stems.
Formation:

- The main crop of cucumbers is tied on the side shoots located on the left and right in the axils of the leaves on the main shoot.Experienced gardeners recommend leaving on the side shoots of the sinuses of the sixth and seventh leaves 3 bundles of ovary, and then pinch the side shoot. On the shoots in the sinuses 8 and 9 of the leaf, 2 bundles of ovary are left, after which they are pinched. On all subsequent lateral shoots (until the end of the fruiting of the bush) leave 1 bunch of fruit ovary.
- Since Cedric has an indeterminate bush, that is, does not have a limited growth point on the main stem, after the plant reaches the upper crossbar of the trellis, pinch the main stem or continue its growth, throwing it on the other side of the trellis and directing it to the ground.
The most successful way to grow cucumbers is to grow in a garter. For this, gardeners use stakes or trellises. They can be both wooden and metal.
 Also gardeners often use a net for climbing plants, mounted on poles dug at the ends of the beds. On a grid or trellis, cucumber lashes are fixed using soft materials, for example, fabric flaps.
Also gardeners often use a net for climbing plants, mounted on poles dug at the ends of the beds. On a grid or trellis, cucumber lashes are fixed using soft materials, for example, fabric flaps.
Soil care
From the very planting of plants into the ground until the end of the growing season, the grower must monitor the cleanliness of the row spacing. When weeds appear, the soil in the aisles must be weeded. Traditionally, in our country, weeding is done with a chopper.
In the last decade, such a weeding tool as the Fokin plane cutter has become very popular among gardeners, it allows you to carry out weeding quickly and without much effort. Weeding is carried out two, and sometimes three times a month, depending on the contamination of the soil with weed seeds.

Periodically, after the past showers, the beds must be loosened. This procedure is designed to destroy the soil crust, which will freely allow heat, air and moisture to penetrate the plant roots.
To reduce physical activity, reducing the number of weeding and loosening - the soil under the bushes and aisles is covered with a thick layer of organic mulch (hay, straw, mowed grass). The mulching layer not only prevents weeds from germinating, but also retains moisture in the soil, which reduces the frequency of watering.
Did you know? In North America in the 18th century, serious magazines and newspapers published articles claiming that cucumbers are harmful to human health. Thanks to these publications, the consumption of cucumbers in the country fell sharply for many years, the popularity of these vegetables revived only in the 19th century.
Pest and Disease Control
The culture of the cucumber is quite gentle and negatively reacts not only to sudden changes in the temperature of the soil and air, but also to the invasion of pests or the appearance of diseases.
The most dangerous pests and diseases of cucumbers:
- Aphids - These are very small insects painted in green, black or white-gray. Pests live in symbiosis with ants, which help aphids to get on plants. Usually pests occupy the upper part of the cucumber bush and young side shoots.
 Aphids feed on juice and leaf cells, which depletes, and eventually destroys, the cucumber bush. As a preventive measure, gardeners spray plantings of cucumbers with bitter herbal infusions, for example, in wormwood, on hot pepper or tobacco leaves. Pests can also be destroyed with insecticides.
Aphids feed on juice and leaf cells, which depletes, and eventually destroys, the cucumber bush. As a preventive measure, gardeners spray plantings of cucumbers with bitter herbal infusions, for example, in wormwood, on hot pepper or tobacco leaves. Pests can also be destroyed with insecticides. - Red spider mite - small insects, in adults the body color is burgundy, and in young animals it is transparent. Even adult insects are not easy to spot on cucumber bushes due to their tiny size (2-3 mm). Their presence on the plant gives out a light cobweb clinging to the leaves and stems.
 On a small number of cucumber bushes, spider mites can be tried to destroy without the use of insecticides, for example, wipe the leaves with warm soapy water or spray with tincture of wormwood. With a large population of cucumbers with a spider mite, the use of insecticides is inevitable. The spider mite feeds on leaf cells. After its nutrition, tiny necrotic spots remain on the leaves, which dry out over time. The massive occupation of plants by the spider mite leads to the oppressed growth of cucumber plantations, deformation and death of leaves, in especially severe cases, and to the death of the bush.
On a small number of cucumber bushes, spider mites can be tried to destroy without the use of insecticides, for example, wipe the leaves with warm soapy water or spray with tincture of wormwood. With a large population of cucumbers with a spider mite, the use of insecticides is inevitable. The spider mite feeds on leaf cells. After its nutrition, tiny necrotic spots remain on the leaves, which dry out over time. The massive occupation of plants by the spider mite leads to the oppressed growth of cucumber plantations, deformation and death of leaves, in especially severe cases, and to the death of the bush. - Tobacco or cucumber mosaic - This is a viral disease, at the moment there are no methods for treating plants. The disease manifests itself in the appearance of stained spots on leaves, where yellow, green, dark green and olive colors may be present at the same time.
 Disease viruses can enter the garden or the greenhouse through seeds, planting containers, garden tools, and on gardener's shoes. In order to exclude the appearance of viral diseases in the garden, it is necessary to take the necessary preventive measures: use only disinfected planting material for sowing, disinfect the garden and garden tools, planting pots for seedlings at the end of the season. You can also decompose the “sanitary buffer” at the entrance to the greenhouse - a cloth dampened in the disinfector, on which incoming people will step on their feet, thereby disinfecting the soles of shoes.
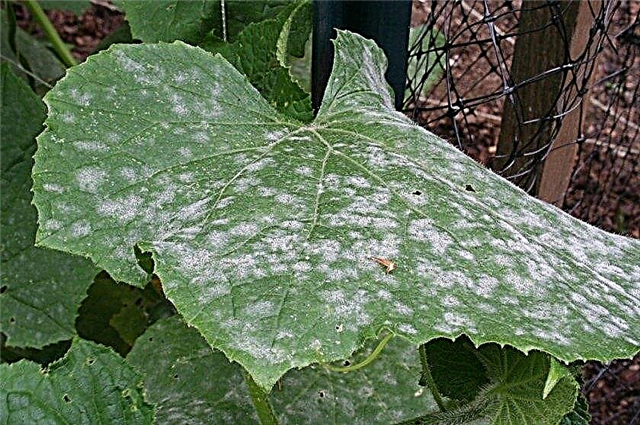
Disease viruses can enter the garden or the greenhouse through seeds, planting containers, garden tools, and on gardener's shoes. In order to exclude the appearance of viral diseases in the garden, it is necessary to take the necessary preventive measures: use only disinfected planting material for sowing, disinfect the garden and garden tools, planting pots for seedlings at the end of the season. You can also decompose the “sanitary buffer” at the entrance to the greenhouse - a cloth dampened in the disinfector, on which incoming people will step on their feet, thereby disinfecting the soles of shoes. - Powdery mildew and peronosporosis Are diseases caused by spores of fungi. With powdery mildew, the leaves of the cucumber are covered with a white fluffy coating, the flowers and developing ovaries die off, the leaves and stems dry out.
 With peronosporosis, dry, rough spots appear on the lower part of the cucumber leaves, the surface of which rapidly increases in size until it merges with neighboring spots, after which the entire leaf dries out.
With peronosporosis, dry, rough spots appear on the lower part of the cucumber leaves, the surface of which rapidly increases in size until it merges with neighboring spots, after which the entire leaf dries out.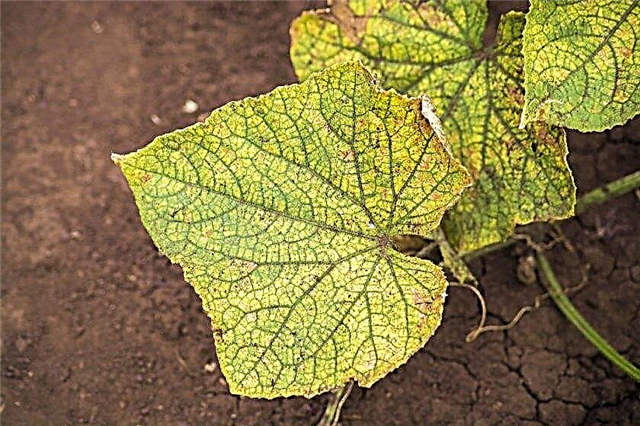  Both diseases are very dangerous for cucumber. Their appearance can be prevented by treating plantings as prophylaxis with fungicides or with a solution of water and sour milk products (whey, kefir, sour milk). Preventive treatments should be carried out weekly, starting from 14 days after transplanting seedlings into the ground. If the cucumber plantation is already sick, it is necessary to treat the plants with fungicides ("Ridomil Gold", "Quadris").
Both diseases are very dangerous for cucumber. Their appearance can be prevented by treating plantings as prophylaxis with fungicides or with a solution of water and sour milk products (whey, kefir, sour milk). Preventive treatments should be carried out weekly, starting from 14 days after transplanting seedlings into the ground. If the cucumber plantation is already sick, it is necessary to treat the plants with fungicides ("Ridomil Gold", "Quadris").
Did you know? About 90% of the mass of the cucumber is water, the remaining 10% are vitamins and minerals useful to the human body.
Harvesting and storage
Harvest cucumbers in a day. It has long been noticed by gardeners that the more often the owner takes ripe cucumbers from cucumber lashes, the faster the new crop grows on the bushes. The fruits are collected in boxes or buckets with smooth walls.

This is an important condition so that the cucumbers do not receive mechanical damage to the skin and do not begin to rot. Cucumber fruits can be stored at a temperature of +10 ... + 12 ° C for 2 weeks. Observing the temperature regime, cucumbers can be transported over long distances.
Hybrid cucumber Cedric F1 differs from other varieties and hybrids in intensive and early fruiting. A dozen cucumber plants can provide a family of 5 people with fresh cucumbers for the whole summer.








 Aphids feed on juice and leaf cells, which depletes, and eventually destroys, the cucumber bush. As a preventive measure, gardeners spray plantings of cucumbers with bitter herbal infusions, for example, in wormwood, on hot pepper or tobacco leaves. Pests can also be destroyed with insecticides.
Aphids feed on juice and leaf cells, which depletes, and eventually destroys, the cucumber bush. As a preventive measure, gardeners spray plantings of cucumbers with bitter herbal infusions, for example, in wormwood, on hot pepper or tobacco leaves. Pests can also be destroyed with insecticides. On a small number of cucumber bushes, spider mites can be tried to destroy without the use of insecticides, for example, wipe the leaves with warm soapy water or spray with tincture of wormwood. With a large population of cucumbers with a spider mite, the use of insecticides is inevitable. The spider mite feeds on leaf cells. After its nutrition, tiny necrotic spots remain on the leaves, which dry out over time. The massive occupation of plants by the spider mite leads to the oppressed growth of cucumber plantations, deformation and death of leaves, in especially severe cases, and to the death of the bush.
On a small number of cucumber bushes, spider mites can be tried to destroy without the use of insecticides, for example, wipe the leaves with warm soapy water or spray with tincture of wormwood. With a large population of cucumbers with a spider mite, the use of insecticides is inevitable. The spider mite feeds on leaf cells. After its nutrition, tiny necrotic spots remain on the leaves, which dry out over time. The massive occupation of plants by the spider mite leads to the oppressed growth of cucumber plantations, deformation and death of leaves, in especially severe cases, and to the death of the bush. Disease viruses can enter the garden or the greenhouse through seeds, planting containers, garden tools, and on gardener's shoes. In order to exclude the appearance of viral diseases in the garden, it is necessary to take the necessary preventive measures: use only disinfected planting material for sowing, disinfect the garden and garden tools, planting pots for seedlings at the end of the season. You can also decompose the “sanitary buffer” at the entrance to the greenhouse - a cloth dampened in the disinfector, on which incoming people will step on their feet, thereby disinfecting the soles of shoes.
Disease viruses can enter the garden or the greenhouse through seeds, planting containers, garden tools, and on gardener's shoes. In order to exclude the appearance of viral diseases in the garden, it is necessary to take the necessary preventive measures: use only disinfected planting material for sowing, disinfect the garden and garden tools, planting pots for seedlings at the end of the season. You can also decompose the “sanitary buffer” at the entrance to the greenhouse - a cloth dampened in the disinfector, on which incoming people will step on their feet, thereby disinfecting the soles of shoes. With peronosporosis, dry, rough spots appear on the lower part of the cucumber leaves, the surface of which rapidly increases in size until it merges with neighboring spots, after which the entire leaf dries out.
With peronosporosis, dry, rough spots appear on the lower part of the cucumber leaves, the surface of which rapidly increases in size until it merges with neighboring spots, after which the entire leaf dries out.  Both diseases are very dangerous for cucumber. Their appearance can be prevented by treating plantings as prophylaxis with fungicides or with a solution of water and sour milk products (whey, kefir, sour milk). Preventive treatments should be carried out weekly, starting from 14 days after transplanting seedlings into the ground. If the cucumber plantation is already sick, it is necessary to treat the plants with fungicides ("Ridomil Gold", "Quadris").
Both diseases are very dangerous for cucumber. Their appearance can be prevented by treating plantings as prophylaxis with fungicides or with a solution of water and sour milk products (whey, kefir, sour milk). Preventive treatments should be carried out weekly, starting from 14 days after transplanting seedlings into the ground. If the cucumber plantation is already sick, it is necessary to treat the plants with fungicides ("Ridomil Gold", "Quadris").