When growing onions, many people have problems associated with its rotting. To achieve such a goal as maintaining a healthy crop, you need to know why onions rot and what is needed to prevent it.
Causes that cause decay
The most important thing is to timely identify the problem of rotting onions. The most common problems are related to soil. In order to preserve the culture, it will be very important to ensure favorable conditions for growth and preservation of the crop.
Excess moisture
All plants have a need for moisture, but you must always follow the norm in watering beds with onions. Waterlogged soil contributes to the development of bacteria and the emergence of various diseases. In the rainy seasons, it is necessary to prepare the drainage to drain excess water from the beds. About a month before harvesting, you need to stop irrigation.
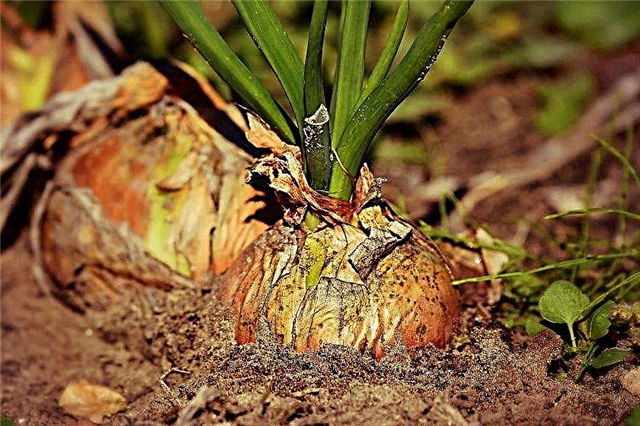

Infected planting material
In order to avoid rotting and preserve the crop, it is necessary to carefully check the purchased planting material. It may well be already infected with an onion infection.
This can be clarified by indicating the following signs of infection:
- wrong color of the covering scales;
- moist top flakes;
- bad smell of set;
- the shell and top of the head are damaged.
Important! It makes no sense to treat the disease, since spores of fungi, bacteria and insect eggs are transmitted through the sowing; after this, the already infected area of the soil will have to be completely treated.
Excess nitrogen in the soil
Another reason for the poor development of the culture is characterized by reduced resistance to disease and growth retardation. Nitrogen is essential for the initial growth of onions. The most suitable sources of nitrogen for it are humus and compost.

They are introduced during the preparation of the soil and have a low concentration, which allows them to evenly expend the elements necessary for the culture. An excess of nitrogen often occurs due to an overdose of fertilizers, so you need to follow the norms and timing of fertilizing.
Onion diseases
Diseases are usually accompanied by fungal or bacterial infections. Causes of illness include high humidity, wet weather and non-compliance with the rules for caring for the crop.
Bacterial soft rot
This disease can be observed on ripened bulbs during harvesting and during storage. The defeat is noticed by the fact that the inner scales soften, become watery in consistency, have a bad smell, yellowish-brown color.

Mostly the lesion goes to separate sections of the onion, and the remaining plates can be healthy. The spread of the disease goes to weakened plants, which become so when the soil is improperly irrigated, due to temperature jumps and a deficiency in the necessary nutrition components.
In order to prevent the onset of this disease, it is necessary to treat onions with special bactericidal preparations containing copper, leave only ripened and dry onions to keep, adhering to the same temperature and humidity.
Did you know? Onions are grown in more than 175 countries, and the total sown area is ahead even of wheat.
Onion bacteriosis
 The disease affects the bulbs in the final process of vegetation, usually on weakened plants and not dried heads, rotting appears from the inside.
The disease affects the bulbs in the final process of vegetation, usually on weakened plants and not dried heads, rotting appears from the inside.
Characteristic features:
- Dun on edible vegetable patches.
- The bulb is soft and mucous.
- Persistent unpleasant odor.
Bacteriosis may be due to waterlogging of the soil, so the only solution is to moisten the soil in accordance with the norm.
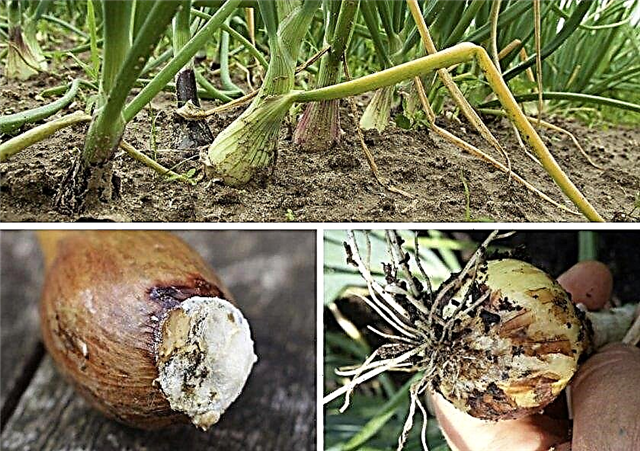
Neck rot
Bulb disease, which is most often manifested during storage, but is affected specifically during the rainy season. The bulb completely decays, the beginning goes from the neck, and then the scales soften, they turn gray.
A gray coating with black dots is seen on the scales and on their surfaces. What should I do? Remove and dry onions in time, observe storage, crop rotation, and seed treatment with fungicides.
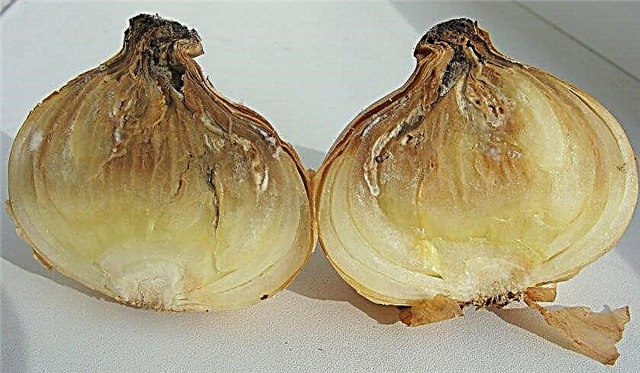
White rot
This onion disease manifests itself in wilting and yellowing of leaves, white fungal formations appear, small black sclerotia appear on the bottom of the onion heads. The spread of the disease goes from external to internal scales. With a severe defeat, the bulbs rot, and then mummification goes on, density and weight are lost.
The main cause of the onset of the disease is soil overmoistening in cold weather, an excess of nitrogen in the soil, acidification and improper crop rotation. It is necessary to combat white rot by treating the culture with fungicides.
Did you know? Onions earned their name due to their apparent resemblance to turnips.
Fusarium rot
The disease is characterized by clear yellowing, deformation and further death of onion leaves. In an infected plant, growth slows down, the roots become brown and then rot. Plants quickly fade, and on the heads, in the region of the base, mycelial filaments are found.
This disease appears in the aggregate from hot weather and soil moisture, and damage to the culture of the onion fly contributes to the appearance of the disease. To prevent it, you need to warm the sevka or pickle it with a fungicide, grow the plant in cool areas.

Powdery mildew
This disease is a fairly common cause of rotting onions. In the plant, green feathers are affected at the beginning, which become chlorous, later yellowing and curvature occur. In dry weather, feathers acquire light green spots, in wet weather, gray-purple mycelium. And then the development of the disease goes to the bulbs and to the root system.
The defeat of this disease can occur due to high humidity and cold weather. To prevent it, it is necessary to exclude nitrogen fertilizers, add a little potassium and phosphorus, and process the bed with preparations containing copper.
Pests
Damage and decay of onions can occur not only with diseases. This culture has its own pests. Onion flies and nematodes cause the most damage to plants, they parasitize in the garden, and therefore the yield will be very bad.
Onion fly
Most damage to the plant is caused by insect larvae. They can gnaw holes in the leaves and bulbs, eat juicy pulp, because of this the bulb heads rot.
 Characteristic signs of onion fly damage:
Characteristic signs of onion fly damage:
- the green feather becomes yellowish;
- holes appear in leaves and bulbs from larvae;
- clearly visible areas where small eggs are debugged.
To prevent the appearance of onion flies, you need to process the garden bed and plants with insecticides, ash, salt or manganese solutions, as well as tobacco dust. Also very effective is the treatment with immunocytophytes.
Stem and bulb nematode
The characteristic signs of the presence of this pest in the culture are reduced in length and thickened leaves, yellow-brown spots and swellings appear.
The beginning starts from the neck, and in the future the feathers die off, the bulbs soften, become soft and light, a light gray color appears, deformation and germination take place. When an infected onion is infected, an unpleasant odor is immediately heard.

Nematodes are tenacious, very active in warm and humid weather. There is no cure for them, the main thing is to adhere to the prevention of pests - to remove weeds, plant debris, crop rotation and warming the seed.
Important! Penetration of nematodes comes from the soil. Often they appear due to infected planting material, water.
What to do and how to deal with it
In addition to the methods that have been described for each specific problem, there are universal methods to combat onion rot:
- disinfect the seeds of the culture chemically or thermally;
- crop rotation compliance;
- remove weeds and loosen the soil;
- properly distribute fertilizers according to their purpose: nitrogen - at the beginning of the development of the plant, phosphorus-potash - at the last stages of the growing season;
- harvest in time - after yellowing of the leaves, when the neck becomes thin and dry;
- dry the onion in the sun, in humid weather - under a canopy (warm up for about 8-10 days, at a temperature of + 25 ° C to + 36 ° C, after which the leaves are trimmed, and the neck should be 5 cm in length);
- promptly sort out the bulbs and remove the infected ones;
- store onions in favorable conditions, temperature from + 18 ° С to + 20 ° С, humidity 60%.
Preventive measures on the beds
In order to prevent and prevent rotting of onions on the beds, preventive measures are needed, which reduces the appearance and development of diseases or pests, protects against crop loss due to any errors in the beginning.

Preventive measures include:
- Crop rotation (return of onions to their original place no earlier than 3-4 years).
- Grow disease-resistant plants.
- Treat seeds and seeds before planting.
- Follow all the rules of agricultural technology.
- To treat the soil and plants with fungicidal and insecticidal preparations, with the appearance of rot.
- Weed and loosen the soil.
- Grow plants next to the onion bed that can deter pests.
The most important thing when growing a crop is proper grooming, normalized nutrition and timely prevention of infection and the propagation of pests. Subject to these rules, onions will not rot in the beds and you will get a healthy crop.












