Among gardeners and summer residents who have taken care not only about the yield on their plot, but also about its appearance, juniper is especially popular. This plant is universally used as the optimal solution in landscape design and gives the estates a special appearance. The wide distribution of juniper is quite understandable - this shrub, having absolute unpretentiousness and winter hardiness, has many varieties. And, perhaps, the most demanded is Andorra Compact - a variety of juniper creeping on the ground that does not lose its beauty, regardless of the season, and therefore is suitable for both single plantings and group compositions.
Botanical Description
According to the description, Andorra Compact Juniper is an evergreen ornamental shrub whose compact crown has a rosette or pillow shape. The needles of the plant are dense and small, the color is green or purple (purple) in the cold season. The diameter of the bush can reach 2 m with a rather low height - about 0.3-0.4 m.
The shoots of the bush are distinguished by a greenish-brown shade, density and elation. The bark of the branches is brown in color, at a young age is smooth and prone to some cracking over time. The root system is well developed, but is located on the surface. Juniper gives fruits of spherical shape, green in color, which later acquire a blue hue and a bluish bloom, which gives the appearance of the plant a special decorative effect.
Important! Due to the strong rhizome, juniper often lands on the slopes to strengthen them.
Landing
Despite the general unpretentiousness, in order for the young juniper bush to be well and quickly taken, you should adhere to the basic principles of planting. First of all, this is the right time for planting. The optimal period for this procedure is considered to be early spring, immediately after the snow melts. However, landing is acceptable in other seasons, but taking into account some features.

For example, in the fall, with early frosts, seedlings may not have time to acclimatize, there is a chance of freezing and their death. In the summer, young bushes will require shading from sunlight. In addition to the right time, you should also pay special attention to the preparation of seedlings, the choice of place and the planting process itself.
Seedling preparation
Due to the poor tolerance of the transplant, it is recommended to choose juniper seedlings with special care.
Important! In order to avoid poor quality of planting material, the purchase of seedlings is best done in specialized nurseries.
In this case, you must pay attention to the following symptoms:
- A plant of 3-4 years is considered the optimal age for transplantation;
- the rhizome of the seedling must be necessarily closed and placed in the substrate (the most suitable containers for this are 5 l);
- the time of acquisition of young bushes is early spring or autumn (it is during this period that the gardener is given the widest selection of planting material);
- during the acquisition process, you should make sure that the needles (its color) correspond to the desired variety;
- unacceptable on the seedlings of bare sites, brown needles, dried tops, affected by diseases and pests fragments.

Site selection and preparation
Juniper is able to grow well on various soilshowever, not very acidic or neutral soils are preferred. These shrubs, like all conifers, will grow well in poor, rocky land. However, good crown development will require a better structure, such as sandy loam soil fertilized with humus.

Placing plants in lowlands, with heavy, dense soil and high humidity, will negatively affect the appearance of the plant. In this case, drought will be preferable to excessive moisture. Stagnation of water carries a particular danger in early spring, and therefore such areas require preliminary drainage and the presence of special ditches to drain excess water.
The best location for planting is any hills or mountains. Like all conifers, juniper needs a lot of sunlight, but creeping varieties, which include Andorra Compacta, tolerate partial shade too.
Landing process
Sapling should be planted with a lump of earth on the roots - this will help the plant to take root faster in a new place. In order to facilitate its removal from the tank, the bush before planting is abundantly watered with water.
Important! In group plantings, the distance between the bushes should be calculated taking into account the diameter of the crown of an adult plant and should not be less than 2–2.5 m.
The landing procedure itself consists of several stages:
- The landing pit is prepared a few weeks before planting - this allows the ground to moisturize and settle evenly. Moreover, its size should be twice as large as the root of a young bush.
- When digging holes, the upper (most fertile) layer of earth is thrown to the side, and then mixed in equal parts with peat and sand. Additionally, the soil can be fertilized with nitroammophos (about 300 g), which is a universal fertilizer and is well suited for all crops in the garden.
- The bottom of the pit is covered with a drainage layer, about 15 cm high. Small stones, broken brick or crushed stone can act as drainage.
- A seedling is put into the hole at right angles and sprinkled with prepared soil mixture. In this case, it is necessary to ensure that the root neck is not deepened and is at ground level.
- The soil is carefully compacted and watered abundantly.

Juniper Care
With its unpretentiousness, juniper does not require much time for care. However, since its appearance will depend on the correct conduct of agricultural activities, minimal procedures will still be needed. These include: watering, fertilizing the soil, loosening and pruning.
Watering
The younger the plant and the less developed its root system, the more often it requires watering. Subject to the presence of rain, water can be completely abandoned from entering the soil. But in dry weather, you will need to water the bushes 2 times in the first month after planting, and then monthly. The method of sprinkling the crown is also applied to the juniper, which should be carried out either in the early morning hours, or after sunset, in order to avoid burns from the sun. Such a procedure can refresh the needles, wash off the dust from it, significantly improving the appearance, and also stimulate the release of volatile, healthy and with a delicate coniferous aroma.
Adult juniper shrubs are recommended to be watered three times per season. Moreover, the volume of water will depend on the degree of root development, as well as on the size of the bush itself, and can vary from 10 to 30 liters per plant. However, you need to know the “golden” rule for growing conifers - it’s better not to top up than to spill.
Top dressing
Despite the fact that under natural conditions, juniper grows in poor soils, modern varieties are more whimsical to the conditions of detention, and therefore require periodic feeding. If during the planting all conditions were met and fertilizers were applied to the land of the planting pit, the bush will not need additional substances for the first two years.
Starting from the third year, annually in the spring it is recommended to introduce complex and mineral fertilizers, according to the instructions. In this case, the plant should be fed not only in the basal circle, but also in the entire growth zone of the rhizome. Such an approach will not only make it possible to replenish all the nutrients in the earth, but will also prevent the development of fungal diseases.
Did you know? Juniper bark was widely used for making dishes in Ancient Russia. The most valuable property was considered the possibility of long-term storage of food products in it without losing their qualities (for example, milk in such dishes did not sour even in the heat).
Loosening and mulching
Loosening and mulching are mandatory plant care procedures that must be performed after each watering or weeding of weed grass. In this case, given the close location of the roots to the surface of the earth, it is recommended to loosen the soil as carefully and shallowly as possible.
Mulching the trunk circle allows you to retain moisture in the soil, prevents the growth of new weeds and the formation of crusts on the surface of the soil, which prevents the flow of oxygen. Moreover, using mulch, you can avoid sunburn of the root system in spring and its freezing in winter. Finely crushed organics, such as sawdust, peat, wood chips, coniferous tree bark or walnut shells, will become the optimal material. The thickness of the mulch layer should not be less than 7–10 cm. Additionally, mulching gives the entire decorative composition a complete look.
Pruning
Due to good tolerance and fast recovery, the following types of pruning are used on juniper:
- Crown formation - allows you to achieve a certain shape of the crown (for example, spherical, pyramidal, etc.), which is especially important in various compositions. However, one should take into account the small annual growth of this plant and not cut the branches too short. The optimal time for this procedure is the first decade of summer, namely: beginning – mid-June.
- Sanitary pruning - In addition to appearance, it is necessary to take care of the healthy development of the shrub, therefore, before wintering and in early spring (before budding), it is recommended to remove from the plant all damaged, deformed or frost-beaten branches.

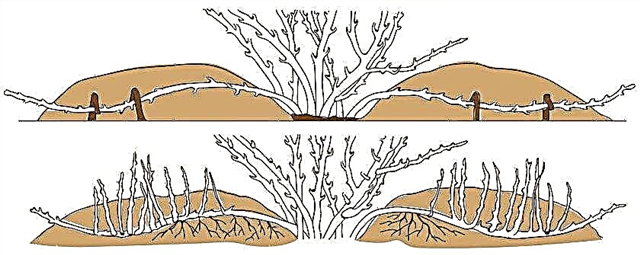
Winter preparations
Juniper belongs to winter-hardy crops, however, in the weather conditions of the Moscow region, young bushes require additional preparation for cold weather. So, bushes, whose age does not exceed 3-4 years, should be covered with winter spruce, and mulch the soil around with sawdust or peat (layer thickness - at least 10 cm). At the same time, with the onset of spring, the mulch must be raked, in order to avoid rooting of the root system.
Juniper with a spreading crown for the winter is not very tightly tied with twine, which will protect the branches from injuries due to the large weight of snow. From above, the plant can be covered with burlap, newspaper or kraft paper, as well as any non-woven material, such as spunbond. Avoid materials that impede the flow of oxygen to the branches of the plant.
It is necessary to remove the shelter with all precautions, given the fragility of the juniper after hibernation. It is better to do this after the earth has completely warmed up (end of April). Adult bushes do not need shelter, moreover, it can lead to undesirable consequences, namely: to the development of fungal diseases that form during the thaws under the covering material. One of the main assistants in preparation for the cold weather is plentiful autumn watering.
Possible diseases and pests
Juniper has a strong immunity to various diseases, and its durable wood is highly resistant to insects. However, there are still diseases and pests, the harmful effects of which from time to time undergo shrubs.
Among them, the most common insects:
- Sawflies - pests, whose larvae, eating shoots and needles, are able to destroy an entire bush, moving from branch to branch. The appearance of insects resembles ordinary green caterpillars with longitudinal dark stripes having eight pairs of legs. The time of their greatest activity is May-June, the life cycle duration is from 20 to 30 days. As a struggle, mechanical influences are used (shaking off larvae from branches and loosening the soil near the juniper), as well as processing with contact insecticidal preparations (the procedure is carried out twice with a break of 2-4 weeks).

- Aphids - small harmful insects, which are dangerous for their high numbers. The plants feed on the juice, which can lead to the complete destruction of the affected areas. Treatment consists in treating bushes with insecticidal drugs, as well as using alternative methods of control - using infusions on laundry soap or tobacco. There are also plants that have the ability to deter these insects. These include feverfew from the Astrov family. In case of small numbers, it is recommended to collect aphids by hand, as well as knock it off the plants with ordinary water under pressure.

- Miners - pests that lay eggs inside the needles. Hatching, the larvae begin to eat the needles from the inside, making moves in it (the so-called mines). In the fight against miners, the affected bushes are treated with insecticides (2 times, with an interval of 2-3 weeks) or sprinkled with shaggy or tobacco dust, which scares them away. Prevention is also important, as autumn digging of the soil around plants is used, as well as removing old bark from bushes and treating all damage with garden varieties.

- Needle tick - a small pest that can be colored yellow, red, green or white. As the first signs of damage, the tips of the needles increased in size can act. As in the cases described above, the treatment of insecticides is the most effective control of insects. However, there is the possibility of refusing chemicals and using folk remedies. For example, watering the juniper crown with warm water and dissolved household soap (the procedure is 2-3 times per season) or using spraying with infusions of tobacco, garlic, horseradish. In this case, the frequency of processing increases to 5-6 times a month.

- Juniper shield - the pest is small, round or oblong, pale yellow. Eating plant juice, such insects can not only significantly slow down the growth of juniper, but also cause its death. At the same time, both the larvae themselves and adult individuals are at risk. As a treatment, damaged fragments are removed from the plant and burned, and the bush itself is treated with insecticides, and also systematically washed with a weak solution of laundry soap, which must then be rinsed with clean running water.

As for diseases, the greatest danger is fungal infections. You can get rid of them only if you diagnose the disease in time and take appropriate measures.
Important! All fragments affected by fungal diseases should not only be removed from the plant, but also burnt. This is due to the high ability to tolerate spores of the fungus over long distances using wind.
Among the common diseases are noted:
- Tracheomycotic wilt (fusarium) - the fungus, which manifests itself in the acquisition of needles of a yellow or red hue, a significant reduction in its quantity and can cause complete drying of the plant. Since the root system is the first to be affected, which ceases to supply the bush with nutrients, it is quite difficult to fight Fusarium. At the first sign, it is recommended to remove all the affected fragments of the bush, and treat the rhizomes with fungicidal preparations.

- Alternariosis - also a fungal disease, the main lesion of which occurs at the roots of juniper.Outwardly manifests itself in the form of a brown shade of needles and gray plaque. As a treatment, all affected branches are removed from the bush, open areas are disinfected with a solution of copper sulfate and smeared with garden var. Prevention is also important - the avoidance of thickening of plantings, as well as the spring treatment of plants with Bordeaux fluid.

- Juniper rust - a fungus whose spores are carried by wind from fruit crops. Outwardly manifests itself in the form of slightly convex spots of orange color, which subsequently crack and become the site of the formation of mycelium. For treatment, treatment with fungicidal preparations can be used (every ten days until recovery), as well as with a solution of Bordeaux fluid. Previously, all affected areas of the bush should be removed. Do not forget about the prevention, which consists in the obligatory gardening of all the wounds on the plant.

- Schütte - fungal disease, which leads to a change in the color of the needles, its drying and falling. The optimal conditions for the development of the disease are increased air humidity and thickening of the crown. Especially often young bushes are susceptible to this disease. As a preventive measure, spring spraying of bushes with Bordeaux liquid is used, collecting fallen needles and removing all damaged branches.

Breeding methods
There are several ways to propagate juniper. All of them have practically equal values in terms of survival, however, the procedures themselves are time-consuming:
- Seed way - juniper cones, which contain seeds, are used as material for obtaining planting material. Having released them, the seeds are soaked in water for one week. In this case, the fluid should be changed as often as possible (at least once a day). As a preparation for sowing, planting material must be stratified - it is preliminarily deepened in a container with sand and placed for 3-4 months on the lower shelf of the refrigerator, or buried in containers with sand in the snow. But the latter option is available only for regions whose weather conditions imply a large amount of snow in winter. In the mid-late spring, the prepared seeds are treated with a growth stimulant and sown to a depth of about 2 cm in the beds or in the greenhouse. At the same time, the soil for sowing should include equal parts of leafy land, peat and humus. Young plants are abundantly watered (if necessary, they can also be planted), and also fertilized with special fertilizing for conifers. Seedlings will be ready for transplanting to a permanent place in the 3-4th year of life.

- Vegetative propagation, or cuttings - An easy way to grow the right amount of planting material. Cutting of cuttings is carried out from late May to early July, and the process itself is carried out using a pruner or hands (breaking out from the base with the heel). In this case, the state of the mother plant should be taken into account - all actions should be carried out as accurately as possible. Depending on the juniper variety, the size of the cuttings will also vary - for small species, 3 cm will be a sufficient length of planting material. Cuttings are planted in a special soil mixture (a composition similar to a substrate for seeds) to a depth of about 1 cm, after being treated with a growth stimulator and antifungal drugs. We should not forget about the mandatory drainage layer in each landing pit. In greenhouses, cuttings spend the whole summer, with regular spraying and ventilation. Throughout the winter period, the seedlings are under cover material, and the planting itself is carried out with the onset of spring.

- Layering - The most suitable and easy way to reproduce horizontal juniper. In the process, the selected side shoots are cleaned of the side branches and strengthened with staples in specially dug ditches, after which they are covered with earth and watered. The prepared layering hides for several weeks with a cut of lutrasil. Over time, the covering material is removed, and the soil around the shoot is loosened, watered and mulched by organic matter. Already next spring, new seedlings can be separated from the mother bush and planted at a permanent place of growth.
Use in landscape design
Juniper looks great both in single plantings and in group compositions, for which it is especially appreciated by landscape designers.
Due to the decorative characteristics and the variety of shapes and colors, this plant is used in various stylistic solutions, the most popular of which are:
- Scandinavian style - simple and somewhat rough, characterized by sharp lines, an open rocky space and restraint: all those features that the harsh northern nature is famous for. In such compositions, juniper allows you to successfully place accents in combination with moss, lichen, heather and other dwarf shrubs.
- Oriental (Japanese) style - compositions with inclusions of bright colors, water, small rocky areas. In this case, juniper bushes emphasize the specifics of the chosen direction and create a contrast.
- English style - restrained and prim, in which the juniper does not stand out in the composition, but serves only as the final element complementing the general landscape.

In any of the options, planting juniper requires adhering to the rules of planting (taking into account the distance between plants, as well as the photophilousness of the bushes). That is why, before planting it in a permanent place, it is recommended that you first arrange the pots with juniper in the area where they are constantly growing, and then make the final decision.
Juniper is characterized by a variety of varieties, appearance and forms. An additional advantage is the availability of planting material, which can be obtained at home independently, as well as the general unpretentiousness of the plant. Such characteristics allow these plants to be planted in areas not only experienced gardeners, but also amateur beginners.Did you know? According to the interpretation of dream books, juniper dreams of wealth and good luck in any endeavors.
























