The use of modern materials and new construction methods make it possible to erect greenhouse constructions in summer cottages on their own for off-season flower cultivation, and also make it possible to increase the reliability of the structure and reduce construction costs. You will find tips and tricks on the construction and equipment of greenhouses in this article.
What greenhouse to choose for growing flowers all year round
If growing flowers is just a hobby, then you can create a mini-greenhouse on the windowsill and grow seedlings of your favorite flowers to create a flower garden in the country. But if you decide to start a profitable flower growing business for sale, you should think about a capital construction.
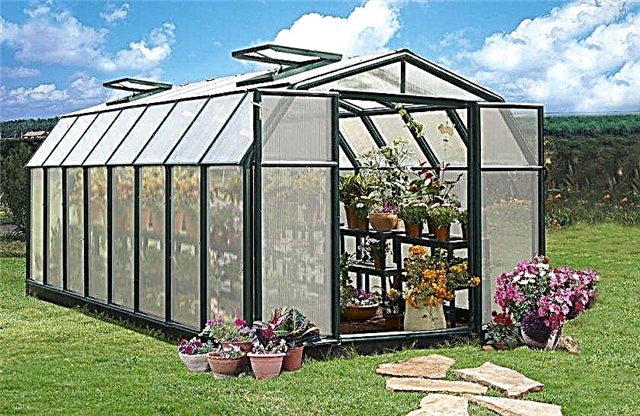

With the advent of new materials and construction technologies, it has become possible to grow flowers all year round, not only in industrial complexes, but also in farms and summer cottages.
For gardeners wishing to start year-round flower growing, just select small greenhouses (100–200 m²). But when choosing a place for a building, it is desirable to leave space for additional structures in order to increase the area in the future.
The choice of a greenhouse depends on such factors:
- climatic conditions of the region;
- type of cultivated seedlings and plants;
- material for construction.
Did you know? The first flower to bloom in outer space at the International Space Station was aster zinnia.
A greenhouse for year-round use must meet the following requirements:
- glass or polycarbonate for coating;
- foundation of concrete, masonry or foam blocks with waterproofing;
- strong arched, single or gable roof for release from snow;
- artificial lighting and heating;
- metal or wooden frame.
Plants require regular watering, optimal temperature and humidity, so the greenhouse must be provided with means to control these indicators.
Choose material
The choice of material for greenhouses is based on a comparison of the positive and negative qualities of the film, glass, polycarbonate and the financial possibilities of the grower.
Film coating
- Pros:
- cost-effective and less costly coverage;
- ease of construction and operation in the future;
- easy to provide ventilation;
- ease of dismantling after seasonal work.

- Minuses:
- frequent replacement of the coating and, as a result, increased costs;
- the possibility of damage during use;
- the coating is not intended for winter cultivation.
A modern version of the film coating is a reinforced film, in which a mesh frame is laid between the layers of polyethylene, which improves the quality and service life.
Glass coating
- Pros:
- excellent translucency (93%);
- low light reflection (4%);
- ease of maintenance;
- environmental friendliness.

- Minuses:
- heavy coating weight;
- fragility and ease of damage.
In regions with a cold climate, double glazing can be used to create the effect of a thermos, but this leads to an increase in the costly item.
Polycarbonate
- Pros:
- translucency (86%);
- high thermal insulation properties;
- strength, flexibility and lightness;
- resistance to natural influences and temperature extremes;
- UV protection;
- fire resistance.

- Minuses:
- instability to degrees;
- heat expansion intensity;
- collapses under the influence of ultraviolet without a special coating;
- abrasive instability (wash without using brushes and abrasive products).
Choose a design
When choosing a design, temperature fluctuations in the area, wind loads, snow resistance and structural strength should be taken into account. The most common and convenient designs: arched, single and gable. An ideal design for a flower greenhouse is a penthouse, the south side of which is lower than the north.
Did you know? The rarest flower on Earth is the red camellia (midleaf red). It grows exclusively in greenhouse conditions in the UK and New Zealand.
Using this design will increase the light and reduce heating. If the north side is laid in blocks or timber, this will protect the greenhouse from the wind and create the effect of a solar battery. The greenhouse on the site should be located in the west-east direction. The frame for the winter greenhouse should be made of wood or galvanized profile, not amenable to corrosion.
Making a greenhouse thermos for growing flowers yourself
Efficiency of use and uniqueness of the design of the thermos greenhouse allow:
- economically use the usable area and grow plants in tight planting conditions;
- high light and heat reflecting properties allow you to save on heating;
- the thermos system maintains the difference between night and day temperatures within 5–7 °, and at midday temperatures of + 50 ° C, + 25 ... + 30 ° C is stored inside;
- high level of illumination even on cloudy days;
- reliability and durability of the structure;
- building elements are resistant to adverse environmental factors;
- the design is easy to assemble;
- plant care comes down to regular dressing and spraying.

The sequence of works on the design of a thermos greenhouse for year-round use can be divided into stages:
- Digging a pit.
- The construction of the walls.
- The formation of the heating system and insulation of the structure.
- The construction of the roof.
- The arrangement of the interior.
The cost of construction depends on such factors:
- dimensions of the structure (height 2–2.5 m, width 5 m, length is optional);
- coverage area on the site;
- the cost of metal parts of the frame;
- sizes of polycarbonate sheets.
Important! During the construction of any foundation, it is necessary to install anchors (bolts, fittings, corners or metal plates), with their help in the future the greenhouse frame is attached to the foundation.
The construction of a thermos greenhouse requires financial and labor costs, so it is important to organize the further cultivation of flowers in order to make a profit.
Foundation work
The main part of the design of the thermos greenhouse is located underground, which provides protection against freezing. The deepening of the lower part of the greenhouse allows you to maintain a positive temperature in the room without additional heating, even in cold weather at -30 ° C. Above ground level are only the top of the greenhouse and the roof. The depth of the pit under the greenhouse should be 2 m, the owner chooses the length based on the need, and the width should not exceed 5 m.

Only with this width is maximum light reflection and heating possible. The foundation pit must be leveled and compacted to build the foundation, the material for which can be timber, brick, concrete or stone. You can fill the foundation for the greenhouse with concrete along the formwork or form the tape method from concrete blocks around the perimeter.
We make and fix the frame
The frame is the "skeleton" of the greenhouse, it must be reliable, strong and durable. When choosing a material for the frame, preference should be given to a metal galvanized profile, which is easy to use, not subject to corrosion and allows you to create a design of any shape (arched, single and gable). For frames and horizontal parts, a U-shaped profile (section 50 × 40 mm) and a guide profile, respectively, are suitable.
Important! The coating should be galvanized on both sides, this is the only way to protect the structure from rust. Polymer-powder or primed coatings are not able to withstand the aggressive climate of the greenhouse for metal.
Arcs can be made from square shaped pipes using a pipe bender. The pipe has good rigidity, does not trap condensate. First, perform the lower harness directly on the foundation for further fastening the frame. Then - the top of the same material, which will simplify the lining and insulation. The number of arcs affects the strength and rigidity of the structure. The location of arcs in increments of 0.5–1 m, depending on the profile characteristics, is considered optimal. The metal for the formation of the carcass is only one third of all the materials used.
Sheathing and insulation of the frame
After the construction of the frame begins the stage of erection of the upper structure - walls of thermal blocks, which are installed directly on the base of the foundation and attached to the metal frame. The thermoblock is a hollow polystyrene foam module, into which concrete is poured with mandatory reinforcement. Such blocks form a monolithic wall with a thickness of 15 cm. On both sides, the wall is obtained with an insulated polystyrene foam surface of 5-10 cm.

The inner surface of the greenhouse must be covered with a special heat-insulating film that reflects infrared radiation in the direction of the source of this radiation. For very cold regions for the winter, it is advisable to use a double layer of foil thermo-reflective film. The purpose of this coating is to maximize the retention of heat and moisture.
After the construction of the walls, you can proceed to the construction of the roof. The universal material for the aboveground part of the thermos greenhouse will be polycarbonate. This material can withstand temperatures from –40 to + 120 ° C, which allows the use of polycarbonate all year round. The sheets are long enough to cover the roof without joints. Due to the heat-reflecting properties of polycarbonate, the heat in the room of the greenhouse is evenly distributed, which allows you to arrange plants throughout the area.
Important! Polycarbonate has a protective layer from ultraviolet radiation. When lining with polycarbonate, the sheet must be installed with a protective layer to the outside, and not otherwise.
Polycarbonate is available in various color shades, which makes it possible to make the greenhouse a decoration of the site. The color of polycarbonate is not important for plants. Inside, it is necessary to achieve complete tightness of the room. To do this, close all the seams of the foundation and thermal blocks with mounting foam and plaster. They also carry out work to provide the greenhouse with electricity, lighting, irrigation and ventilation systems, and install heating systems.
We make a heating system
The decision to grow flowers year-round is inextricably linked with heating the greenhouse in the winter. The choice of heating systems is based on an assessment of the positive and negative characteristics of each type.
Electric heating
This type of heating is characterized by:
- highest efficiency;
- simplicity;
- high level of automation;
- lack of harmful gases;
- the cleanliness of the microclimate of the greenhouse.

Heating is carried out by convectors, heaters, cables or infrared installations. The disadvantages include a possible breakdown of the devices, and it is better to entrust the laying of cables for heating to a specialist.
Stove heating
- The advantages of this heating method are:
- profitability;
- reliability;
- a large selection of energy sources (firewood, coal, gas).
Important! When organizing the furnace method, it is possible to equip the outlet of flue gases through the ground, which will lead to additional heating.
- The disadvantages include:
- lack of automatic temperature control;
- heating the outer walls of the device;
- the possibility of leakage through rusty pipes.
Pipe heating
It is a water boiler installed in the vestibule. The water in the boiler is heated by firewood, coal, peat or gas, and the greenhouse is heated by a system of polypropylene pipes. To adjust the temperature of the pipe is equipped with valves.

This method requires constant temperature control in order to avoid damage to the root system of plants, but the absence of heating devices in the greenhouse frees up usable area.
Combined method
With such an organization, heating occurs from above with infrared rays, and from below with a system of pipes, which provides high automation of temperature control. Dark sheets of roofing material in the aisles and outside the perimeter will help to keep warm. Any greenhouses need a ventilation system, and in the summer hot days you can adjust the temperature using the blinds.
Did you know? A fourth of the area of the Netherlands is occupied by greenhouses - 10.5 thousand hectares.
What flowers to choose for growing
It is impossible to unequivocally answer the question of which flowers are better to choose for growing. Each variety is unique in its own way, and the demand in the flower market is constantly changing. Profit from the flower business depends on the season - summer demand for flowers is lower than in winter. It is necessary to distinguish between flowers that are grown under the cut for bouquets and the cultivation of flower seedlings.

Let us dwell only on some names of flowers from the whole variety:
- Roses - Flowers can easily tolerate greenhouse cultivation, but they need good lighting and a sufficient amount of moisture. You need to plant roses at a distance of 30 cm from each other for good ventilation of the plants. Propagated by cuttings.
- Tulips - the quality of the flowers depends on the seed: the larger the bulb, the larger the flower.
- Lilies - In the greenhouse, tiger and royal species are most often grown. Lilies require nutritious, well-moistened soil, drainage is mandatory. Propagated by bulbs.
- Crocuses - corms of various colors, personify the onset of spring.
- Chrysanthemums - delight flowering until late autumn, and in a greenhouse, flowering increases up to three times a year.
- Daffodils - You can plant in late autumn after frost.
- Asters - You can grow both annual and perennial plants.
- Dahlias - they admire the abundance of shapes and colors, look very profitable in any bouquet.
- Hyacinths - can be grown and cut, and in pots for sale.
Important! Tulip bulbs must be cooled before planting, otherwise they will not germinate.
For the sale of flower seedlings, nasturtiums, pansies, marigolds, petunias, snapdragons are suitable. The greenhouse complex allows you to grow indoor plants with further sale - palm trees, oleanders, ficus, potted flowers. It is advisable to buy seeds and seeds at specialized flower shops in order to avoid fakes and not to be mistaken with the selected variety. Seasonal flowers can be planted alternately and combined with other plants.
How to place plants in a greenhouse
The internal arrangement of the greenhouse is reduced to the formation of beds, walkways, installation of racks and shelves. It is advisable to make a map of the location of plants and flowers in advance, which will facilitate a more harmonious layout on the spot.

Standard layouts of beds and plants are as follows:
- flower beds make high;
- allocate parallel beds for flowers of the same species;
- partitions are installed between different types;
- the construction of racks and shelves creates the possibility of floor placement of plants;
- tall plants are located on the north side of the room, and low - on the south;
- ampelous plants are located above human growth;
- for climbing plants, it is advisable to pull a wire or twine;
- Planter brackets are firmly attached to the frame.
Starting to engage in year-round flower growing, you should prepare for the constant care of them. Plants in the greenhouse require constant transplantation, caring for crops, pruning and gartering, fertilizing and fertilizing. It is necessary to follow the data of the microclimate in the room, to ensure the correct heat and light, regular watering and spraying.Did you know? On 1 m² of greenhouse space you can plant two dozen daffodils, tulips, hyacinths or 100 daisies.
Flowers delight us on weekdays and on holidays. Not a single celebration is complete without flowers. The right choice of a greenhouse, construction and equipment of a greenhouse, and a careful selection of varieties for growing flowers throughout the year will help turn an exciting hobby into a profitable business.